LeetCode75
You have a long flowerbed in which some of the plots are planted, and some are not. However, flowers cannot be planted in adjacent plots.
Given an integer array flowerbed containing 0's and 1's, where 0 means empty and 1 means not empty, and an integer n, return true if n new flowers can be planted in the flowerbed without violating the no-adjacent-flowers rule and false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1 Output: true
Example 2:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 2 Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= flowerbed.length <= 2 * 104flowerbed[i] is 0 or 1.flowerbed.0 <= n <= flowerbed.lengthflowerbed داریم که شامل 0 و 1 است:1 یعنی جای گل کاشته شده.0 یعنی جای خالی.n گل جدید بکاریم یا نه.flowerbed حرکت میکنیم و بررسی میکنیم که آیا در i میتوان گل کاشت یا نه.iام:خانهی i باید 0 باشد.i-1) و بعدی (i+1) هم 0 باشند (یا خارج از محدوده باشند).flowerbed[i] را 1 میکنیم و n را یکی کم میکنیم.n == 0 شد، یعنی گلها را کاشتیم و باید True برگردانیم.n هنوز مثبت بود، یعنی نشد همه گلها را بکاریم، پس False برمیگردانیم.کد پایتون (با کلاس Solution):
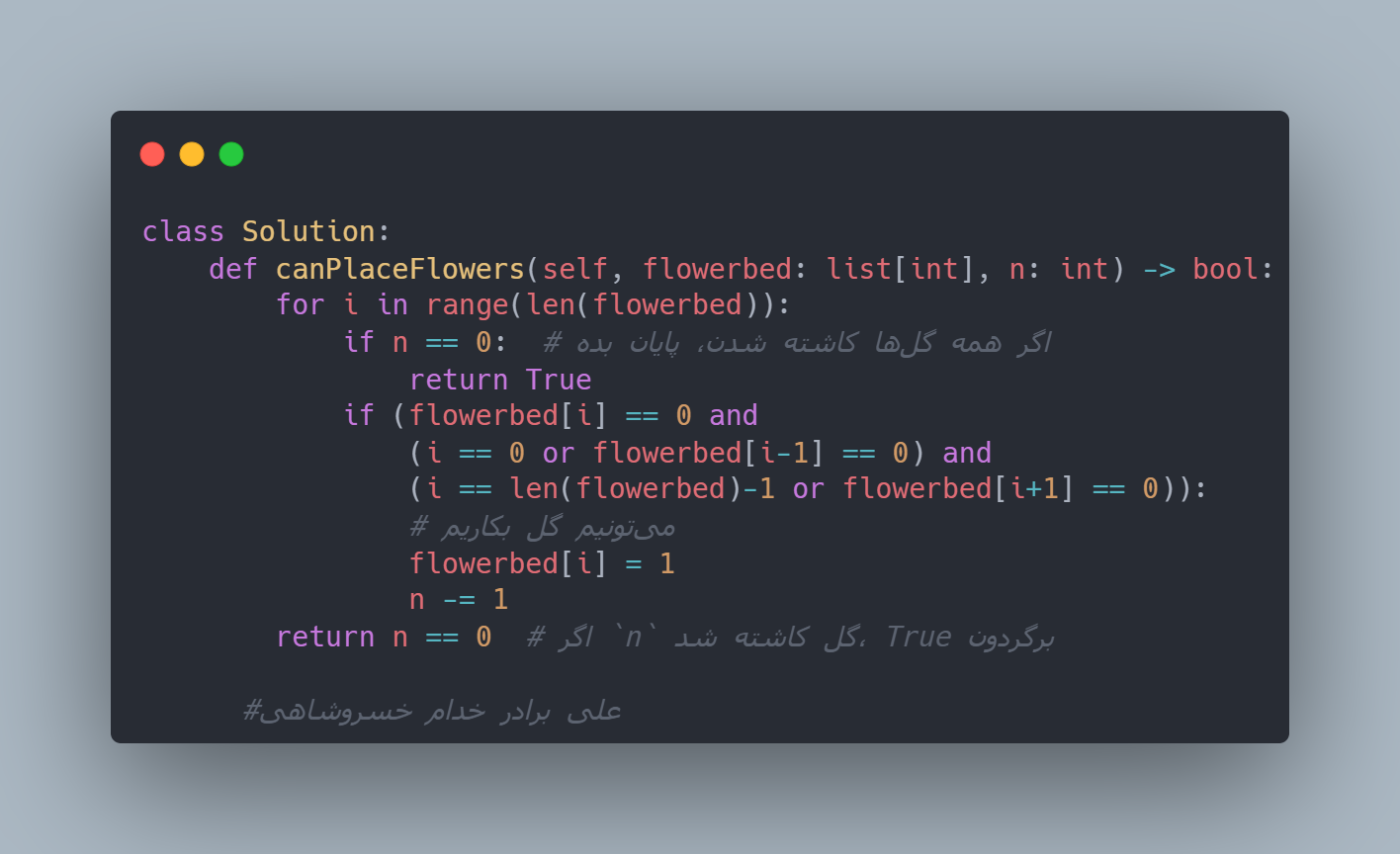
class Solution:
def canPlaceFlowers(self, flowerbed: list[int], n: int) -> bool:
for i in range(len(flowerbed)):
# اگر همه گلها کاشته شدن، پایان بده
return True
if (flowerbed[i] == 0 and
(i == 0 or flowerbed[i-1] == 0) and
(i == len(flowerbed)-1 or flowerbed[i+1] == 0)):
# میتونیم گل بکاریم
flowerbed[i] = 1
n -= 1
# اگر `n` گل کاشته شد، True برگردون
return n == 0
#علی برادر خدام خسروشاهی
flowerbedبررسی میکنیم که آیا میتوان در i گل کاشت یا نه.i، i-1، i+1 صفر باشند.flowerbed[i] را 1 میکنیم و n -= 1 انجام میدهیم.n == 0 شد، یعنی کافی بوده و True برمیگردانیم.n > 0 باشد، False برمیگردانیم.✅ زمان اجرای O(n)
✅ بدون لیست اضافی (O(1) فضای اضافی)
flowerbed تغییر میدهیم، پس حافظه اضافی مصرف نمیکنیم.✅ مؤثر و ساده
حالا تو هم میتونی مثالهای خودت رو تست کنی! 🚀😊
علی برادر خدام خسروشاهی