برگرفته ازسایت
خوب می خواهیم یک شکلی درون صفحه ی وب حرکت کند یا حرکت داده شود.
قبلا مگه درمورد این مسئله کارنکردیم وگفتیم که فضای صفحه ی وب دوبعدی است و فضایی که هرچندبعدی بسازیم یا بسازی همان دوبعد باقی می ماند ومعنی خاصی درفضای چندبعدی درصفحه ی وب یا اچ تی ام ال چندبعدی وجود نداردیانداره.

اینه
javascript animation mathematical vector space model
موضوعش.
یعنی همین قسمت یک مرورگرهمان فضای برداریه؟
نمی دونم این مسئله را خیلی گسترده شد.
ولی این را می دونم
یعنی یک برداراین همه ویژگی/مقداریاابعاد داردیا داره؟
shown as a transparent mesh.
At the start two vectors will be visible, a with red filling color of the arrowhead, b with white color.
At the left side one can chose among different perspective projections by radio buttons:
perspective: 3D projection with perspective distortion. It can be rotated with the mouse.
xy-projection: top view of the xy-plane (along the z-axis)
yz-projection: along the x-axis
xz-projection: along the y-axis
no perspective: 3D projection without distortion. It can be rotated with the mouse.
At the bottom the following data are shown for the 2 vectors a and b
Intersecting angle: in degrees.
Product of absolute values: always 1, as both are of length 1.
Scalar product: a∙b = a| |b| cos(a|b), with a|b the intersecting angle.
Absolute value of the vector product: |a x b| = |a| |b| sin(a|b).
At the top the following operations can be activated by check boxes:
Addition: a + b.
Subtraction: a - b.
Subtraction: b - a (= -(a - b)).
Vector product: a x b.
Vector product: b x a (= - a x b).
3 Vectors a + b + c: generation of c and sum (c with yellow filling color).
The chosen combination is maintained when new vectors are generated.
Vector calculus
Vectors
a = (a1 , a2 , a3)
b = (b1 , b2 , b3)
Absolute value (length of the vector arrow) |a| = √(a12 + a22 + a32 )
Addition a + b = (a1+b1 ,a2+b2 , a3+b3) = b + a
Subtraction a - b = (a1 -b1 ,a2- b2 , a3- b3)= - (b - a)
Subtraction b - a = (b1- a1 , b2- a2 , b3- a3) = - (a - b)
Multiplication by a constant k: ka = (ka1 , ka2 , ka3)
Skalar product (internal product) a · b = a1b1 +a2b2 + a3b3 = |a| |b| cos(a|b)
a perpendicular to b ⇒ a|b = 90o ⇒cos( a|b) = 0 ⇒ Scalar Product = 0
Vector product (external product) a x b = (a2b3-b2a3 , a3b1 - b3a1 , a1b2 - a2b1)
Vector product b x a= (b2a3- a2b3 , b3a1 - a3b1 , b1a2 - a1b2) = - a x b
Absolute value of vector product |a x b| = |a| |b| sin(a|b)
برای حل این مسئله فشارخیلی زیادی به بدنم و پاهایم و ریدن ام گرفت برای حل کردن این مسئله وحتی تحقیق کردن درموردش.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="fa"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Vector Space Shape</title> <style> body { background:#111; display:flex; justify-content:center; align-items:center; height:100vh; } canvas { background:#000; border:2px solid #fff; } </style> </head> <body> <canvas id="c" width="600" height="600"></canvas> // ---- فضای برداری ----- // تعریف یک کلاس برای بردارها (R^2) class Vec { constructor(x, y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } add(v) { return new Vec(this.x + v.x, this.y + v.y); } mul(a) { return new Vec(this.x * a, this.y * a); } } // ---------------------- // بردار موقعیت پارامتریک r(t) function r(t) { let v1 = new Vec(Math.cos(3*t), Math.sin(3*t)).mul(150); let v2 = new Vec(Math.cos(t), Math.sin(t)).mul(50); return v1.add(v2); // ترکیب خطی → a*v1 + b*v2 } // ---------------------- let canvas = document.getElementById("c"); let ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"); function draw() { ctx.clearRect(0,0,600,600); ctx.translate(300,300); // مرکز مختصات ctx.strokeStyle = "cyan"; ctx.lineWidth = 2; ctx.beginPath(); let start = r(0); ctx.moveTo(start.x, start.y); for (let t=0; t<Math.PI*2; t+=0.01) { let p = r(t); // بردار موقعیت ctx.lineTo(p.x, p.y); } ctx.stroke(); ctx.resetTransform(); } draw(); </body> </html>کد کامل: HTML + CSS + JavaScript (بردار از صفر تا صد) index.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="fa"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Vector Space Shape</title> <style> body { background:#111; display:flex; justify-content:center; align-items:center; height:100vh; } canvas { background:#000; border:2px solid #fff; } </style> </head> <body> <canvas id="c" width="600" height="600"></canvas> // ---- فضای برداری ----- // تعریف یک کلاس برای بردارها (R^2) class Vec { constructor(x, y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } add(v) { return new Vec(this.x + v.x, this.y + v.y); } mul(a) { return new Vec(this.x * a, this.y * a); } } // ---------------------- // بردار موقعیت پارامتریک r(t) function r(t) { let v1 = new Vec(Math.cos(3*t), Math.sin(3*t)).mul(150); let v2 = new Vec(Math.cos(t), Math.sin(t)).mul(50); return v1.add(v2); // ترکیب خطی → a*v1 + b*v2 } // ---------------------- let canvas = document.getElementById("c"); let ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"); function draw() { ctx.clearRect(0,0,600,600); ctx.translate(300,300); // مرکز مختصات ctx.strokeStyle = "cyan"; ctx.lineWidth = 2; ctx.beginPath(); let start = r(0); ctx.moveTo(start.x, start.y); for (let t=0; t<Math.PI*2; t+=0.01) { let p = r(t); // بردار موقعیت ctx.lineTo(p.x, p.y); } ctx.stroke(); ctx.resetTransform(); } draw(); </body> </html>
نتیجه:
چیزی که درون فضای وب یا اچ تی ام ال مشاهده می کنید
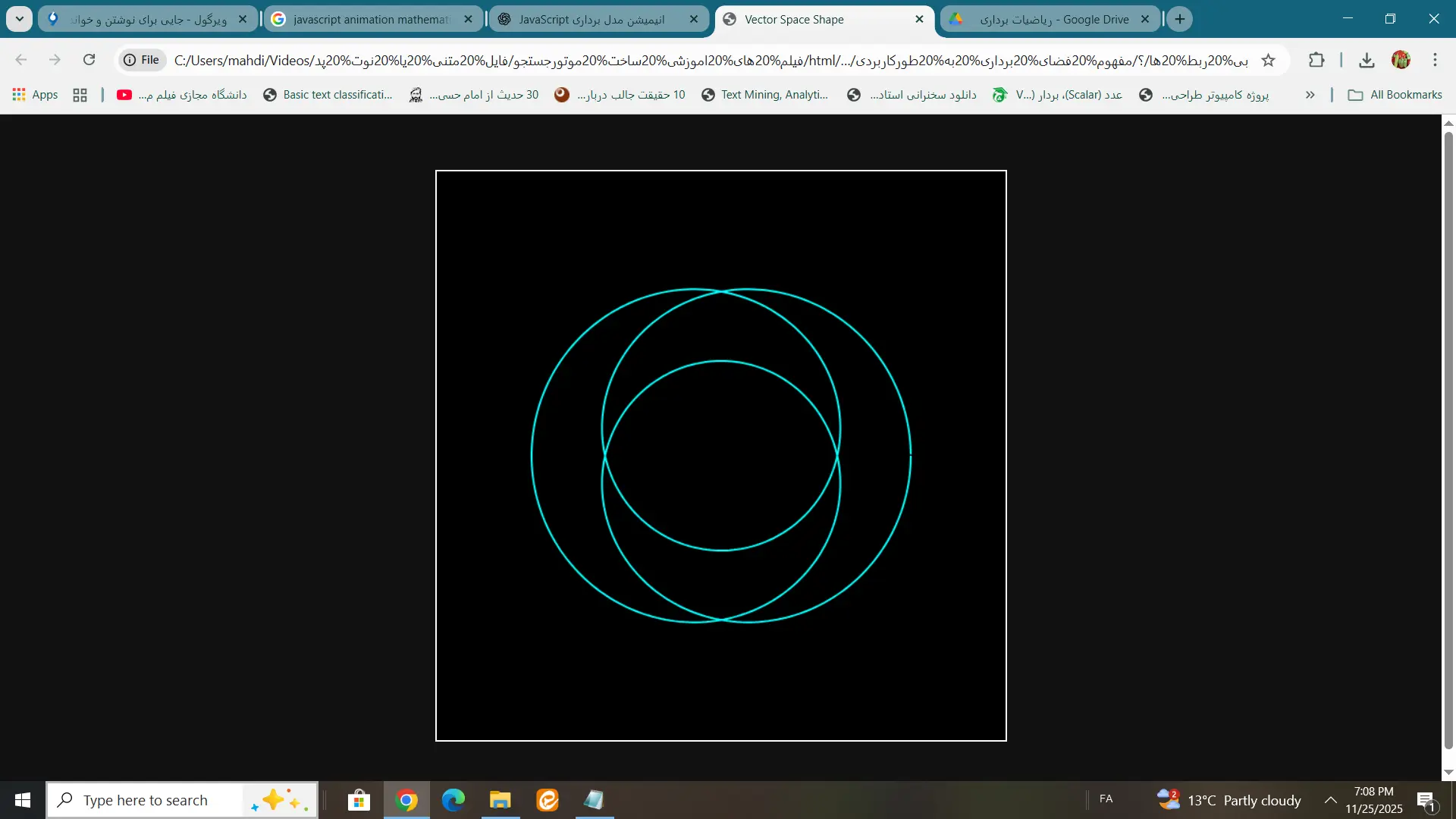
مسئله من دراین قسمت می باشد:
class Vec { constructor(x, y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
بقیه کد مسئله ی خاصی نداره یا ندارد.
اینها توابع ازقبل تعریف شده می باشد
Math.cos()
Math.sin()
خوب اینها هم بردارهایی هستند که چجوری ساخته شده اند نه سینوس وکسینوس که ربطی به بردارها ندارند اینها توابع هستند یعنی توابع ربطی بردارها وفضای برداری ندارند نه فقط یک ورودی میگیرند یک خروجی می دهند.
من دیگه موضوع تحقیق ام راپیدا کرده ام یا کردم اگر فرداصبح ازخواب بیدارشوم یادم نرفته باشد یا دیگه اثری ازش نباشد.
بگذاریکم روی نتایج این کدها کارکنیم شاید چیزی دستگیرمان شد.
خوب این کدها کجا اجرامی شوند؟
شما وقتی داخل مرورگرتان کلیک راست کنید وروی گزینه ی
inspector
كليك كنيد روی گزینه ی کنسول کلیک کنید می تونید کدهای جاوااسکریپتان را اجرا کنید حالا می خواهیم بدانیم یا ببینم چطوری کلاس بردارمی سازد درون جاوااسکریپت.
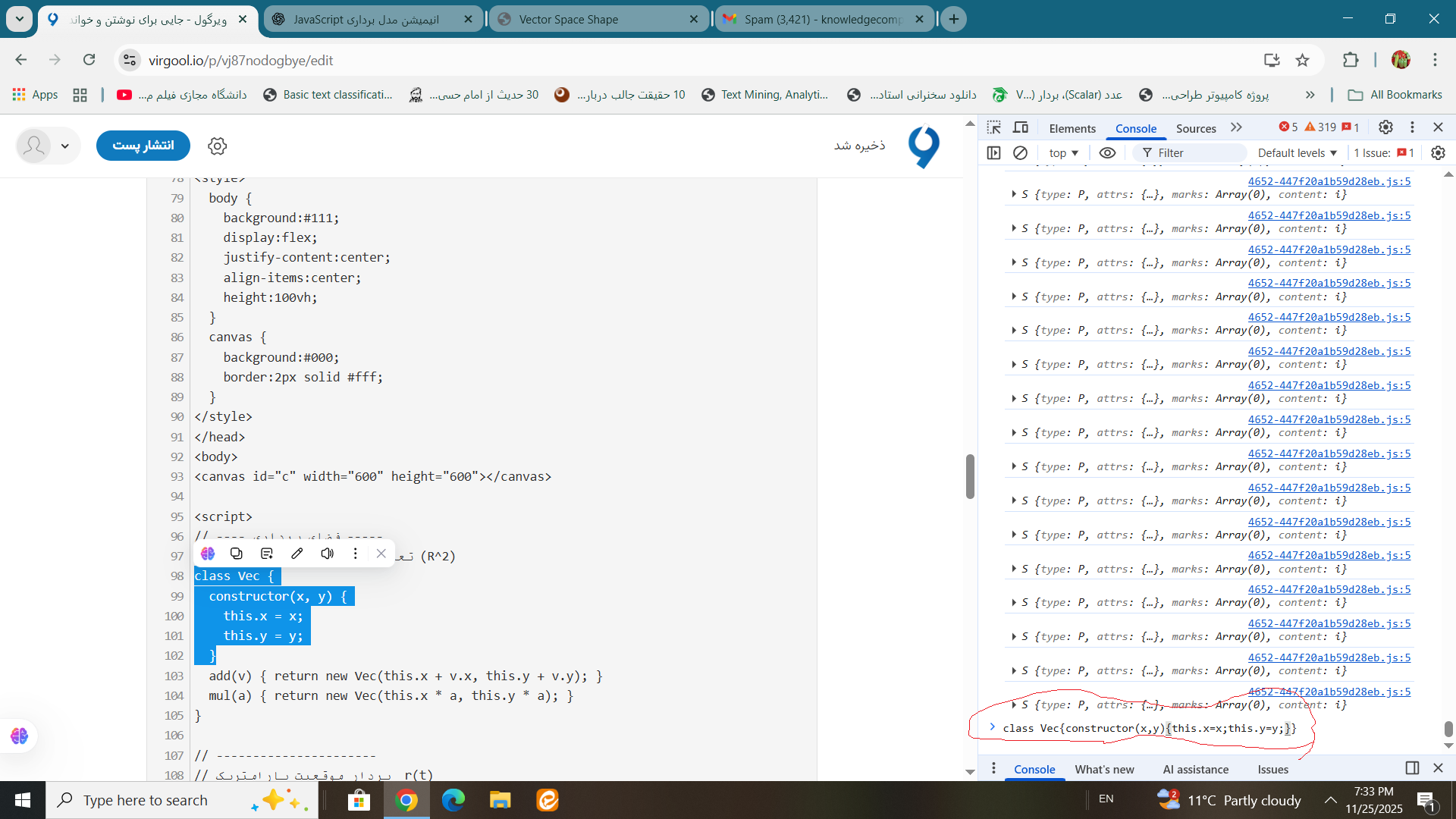
ببینیم خروجی به ما چی می دهد.
هوش مصنوعی اوپن اِی آی می گوید این قسمت بردارهای تشکیل شکل رامی سازند
function r(t) {
let v1 = new Vec(Math.cos(3*t)*150, Math.sin(3*t)*150);
let v2 = new Vec(Math.cos(t)*50, Math.sin(t)*50);
return new Vec(v1.x + v2.x, v1.y + v2.y);
}
نه این قسمت
class Vec { constructor(x, y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }
من ازاین به بعد روی این کدهایم کارمی کنم شما هم روی موضوعات خودتان مثل ساخت مامان و مادروباباوبچه برای دیگران کارکنید قبوله!
کلاازاین قسمت و کدنویسی می خواستی به چه نتیجه ای برسی کمی به گذشته ام رفتم ببینم وضعیت ام چطور شده است ازلحاظ ارتباطی.
حالا بعدا این قسمت را بررسی می کنیم که چه اتفاقی می افتد که باعث می شود بردار یک شکل ساخته می شود یاشود.
Math.cos(3*t)*150, Math.sin(3*t)*150
Math.cos(t)*50, Math.sin(t)*50
یا این قسمت تابع
// ---------------------- // بردار موقعیت پارامتریک r(t) function r(t) { let v1 = new Vec(Math.cos(3*t), Math.sin(3*t)).mul(150); let v2 = new Vec(Math.cos(t), Math.sin(t)).mul(50); return v1.add(v2); // ترکیب خطی → a*v1 + b*v2 }
یا اصلا این تی ازکجا اومده است یا چطورساخته می شود یا معنی اش چیه یا علت این که این تی باعث ساخته شدن بردارمی شود یا شده است چی است یاهست.
خوب دراین مسئله ما تی را مشخص کنیم می تونیم به خیلی چیزها برسیم.
موفق باشید
به امیدخدا